Home Hardening
Why is Home Hardening Important?
About 4,000 houses are destroyed by wildfires in the USA each year. One method to prevent your home from becoming one of them is home hardening. This is the process of managing landscaping, building materials, and basic maintenance to make your home as safe as possible and create a defensible space to fight the ever-growing danger of wildfires
Creating a Defensible Space
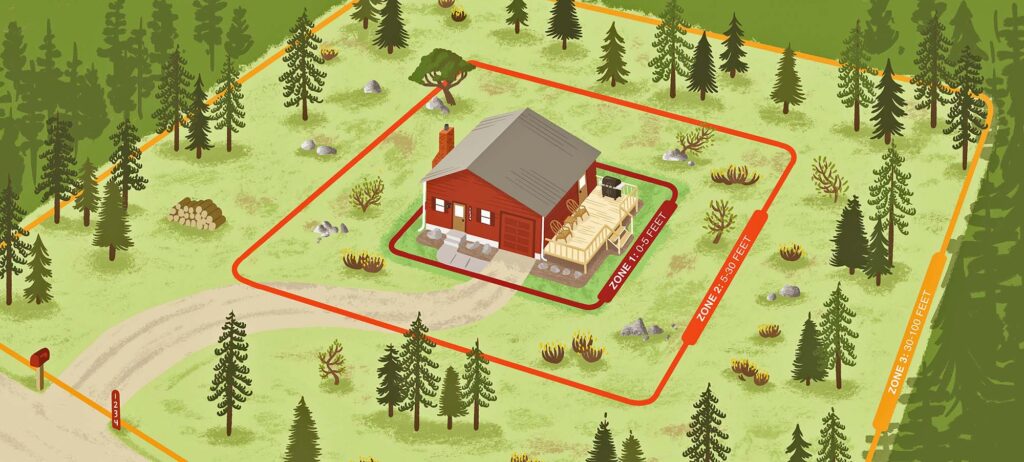
The Immediate Zone
The immediate zone stretches from 0-5′ and is the most important of the three parts. There are many ways to help manage this area, starting first with the house. Prevention methods related to a structure include using fire-resistant materials. Homes should also be surrounded by a 2-3′ barrier of fire-resistant mulch. A study conducted by The University of Nevada about mulch combustibility found that the most effective barrier was composted wood chips. Unlike the other mulches tested, this did not produce a steady flame but rather smoldered with incidental flame. Rubber mulch produces the hottest temps and highest flames. For more information, visit This Link
The Intermediate Zone
The intermediate zone stretches 5′-30′ from the structure. Preventative measures in this area include practices such as creating driveways, sidewalks, or patios to serve as fuel breaks in between vegetation. Another important practice is trimming trees. branches should be pruned back by about 6-10 feet off the ground, or 1/3 the height of a smaller tree. Trees should also be spaced about 18 feet between crowns, or the branches. All dead and dry vegetation material should also be removed.
Extended Zone
The extended zone extends from 30′ to 100-200′. All dry vegetation should be removed in this area. Any structures like sheds, play sets, RV’s, or vehicles should have a 5′ ember-resistant zone. This includes removing vegetation and dry materials as well as spacing trees from them. Tree placement is a critical part of creating a defensible space. in the extended zone, trees should be spaced out 6-12 feet or more, depending on species or slope.
Preparing Your House: Home Hardening Tips
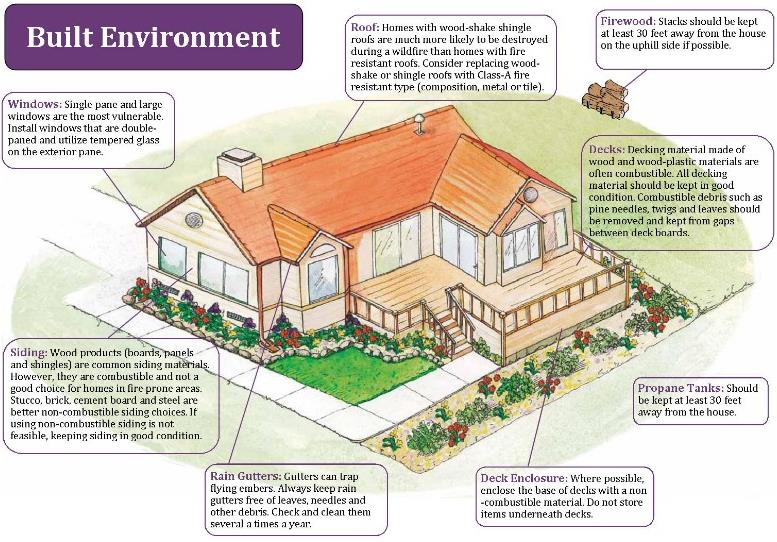
There are many important steps to hardening your house against wildfires that go beyond creating a defensible space around the structure. Much of this involves proper building materials and regular maintenance of things such as siding, roofs, vents, windows, etc. Here are some proven techniques to better prepare your house.
Roof
The home’s roof is the most vulnerable to flying embers and sparks, making it one of the most important parts to fireproof. Hardened roofs should be made up of fire-resistant materials, such as asphalt or tile. All shingles should have a Class-A fire rating. Gutters should also be clear of leaves and debris, as this is an extreme fire hazard. Gutter covers can also be an option to prevent debris from entering. Eaves should be outfitted with soffits made from fire-resistant materials to prevent embers from entering.
Vents and Windows
Vents are an easy entrance for sparks and embers to enter and flare up if proper measures aren’t taken. 1/8″ to 1/16″ inch mesh should be put over all vents to prevent sparks from entering. Windows should be dual-paned, and made of tempered glass. This will make them more resistant to breaking when exposed to extreme heat.
Decks
All decks, patios, porches, etc. should be built out of non-flammable materials. Composite decking, often made from a combination of wood flakes and polymer plastic, is a great alternative to the traditional wood deck, which can turn into a serious fire hazard. Any outdoor furniture, such as picnic tables, lawn chairs, etc. should also be made of fire-resistant materials.
Siding and walls
Using fire-resistant materials such as cement or stucco is a great way to harden your house against wildfires. These are both great alternatives to materials such as wood. Where your address is placed is also a very important and often overlooked aspect. The address numbers should be visible from the road for emergency vehicles.
Overview
Overall, the biggest part of home hardening is being smart and vigilant. Much of preparing against wildfires is managing landscaping, such as keeping grass and vegetation mowed down as well as properly spacing and trimming trees It also includes regular maintenance of, as well as proper materials for siding, roofs, windows, and decks. As long as these key components are taken care of, your house should be as prepared as possible for the next wildfire. For more information, click on the links below
Further Information
Colorado State Forestry-Wildfire Mitigation Project
Barnyards and Backyards-Wildfire Recourses
University of Nevada- Mulch combustibility